
The Deep Web is fundamentally referred to data which are not indexed by any standard search engines as e.g. But what separates the hidden parts into Deep Web and Dark Web by definition?

The remaining 96% (90% + 4%) are protected by passwords, hidden behind paywalls or can be accessed via special tools (Hidden Internet 2018). This huge amount of data can be separated into three parts: Separation of the worldwide web, Reference: (Search Engines 2019)Īs seen in the picture above, we are accessing only 4% available on search engines like Google or Bing. The internet as most people know it, forms only a minimal proportion of the overall 7.9 Zettabyte (1 ZB = 10007 bytes = 1021 bytes = 1000000000000000000000 bytes = 1 trillion Gigabytes?) of data available online (Hidden Internet 2018). So, what exactly is the deep web? To explain this, it makes sense to cast a glance at the overall picture. Reference: Giphy, If Google was a person: Deep Web

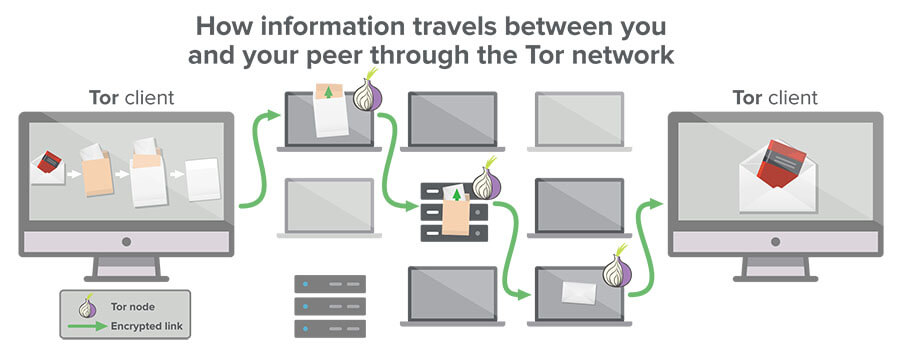
This blogpost aims to shed light into the dark corners of the deep web and primarily deals with the explanation of how TOR works. But in times of continuous tracking on the Internet, personalized advertising or digital censorship by governments, the (almost) invisible part of the web promises to bring back lost anonymity and privacy as well. The mysterious dark part of the internet – hidden in depths of the world wide web, is well known as a lawless space for shady online drug deals or other criminal activities.
Written by Tim Tenckhoff – tt031 | Computer Science and Media 1.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
